Archives
- 2025-10
- 2023-07
- 2023-06
- 2023-05
- 2023-04
- 2023-03
- 2023-02
- 2023-01
- 2022-12
- 2022-11
- 2022-10
- 2022-09
- 2022-08
- 2022-07
- 2022-06
- 2022-05
- 2022-04
- 2022-03
- 2022-02
- 2022-01
- 2021-12
- 2021-11
- 2021-10
- 2021-09
- 2021-08
- 2021-07
- 2021-06
- 2021-05
- 2021-04
- 2021-03
- 2021-02
- 2021-01
- 2020-12
- 2020-11
- 2020-10
- 2020-09
- 2020-08
- 2020-07
- 2020-06
- 2020-05
- 2020-04
- 2020-03
- 2020-02
- 2020-01
- 2019-12
- 2019-11
- 2019-10
- 2019-09
- 2019-08
- 2019-07
- 2019-06
- 2019-05
- 2019-04
- 2018-07
-
DiscoveryProbe™ FDA-approved Drug Library: Transforming C...
2025-10-23
Explore how the DiscoveryProbe™ FDA-approved Drug Library enables unprecedented cell-based drug repositioning and pharmacological target identification. This article reveals advanced screening strategies, integrating recent mechanistic breakthroughs for translational biomedical research.
-
DiscoveryProbe FDA-approved Drug Library: Transforming Hi...
2025-10-22
The DiscoveryProbe™ FDA-approved Drug Library accelerates translational research with a ready-to-screen collection of 2,320 clinically validated compounds. Its versatility in high-throughput and high-content screening empowers drug repositioning, target identification, and advanced disease modeling across oncology, neurology, and rare diseases.
-
GDC-0941: A Selective PI3K Inhibitor for Translational On...
2025-10-21
GDC-0941 is a highly selective class I PI3 kinase inhibitor optimized for robust PI3K/Akt pathway inhibition, including in trastuzumab-resistant HER2-amplified cancer models. This guide details advanced experimental workflows, troubleshooting insights, and comparative advantages, empowering researchers to maximize the translational impact of GDC-0941 across in vitro and in vivo oncology studies.
-
Strategic Horizons in EZH2/PRC2 Inhibition: Leveraging GS...
2025-10-20
This thought-leadership piece provides translational researchers an advanced, integrative perspective on EZH2/PRC2 inhibition, spotlighting GSK126’s mechanistic precision and strategic utility in oncology and epigenetics research. Moving beyond conventional product narratives, it contextualizes GSK126 within novel regulatory paradigms, including lncRNA-mediated EZH2 modulation, and frames actionable guidance for experimental design, workflow optimization, and the next wave of clinical translation.
-
Redefining Cancer Epigenetics and Immunoepigenetics: Stra...
2025-10-19
This thought-leadership article explores the transformative role of GSK126—a selective EZH2/PRC2 inhibitor—in advancing oncology and immunoepigenetics research. We blend mechanistic insights into histone H3K27 methylation and inflammasome regulation with actionable guidance for translational investigators. Integrating recent breakthroughs, including the epigenetic control of inflammasome activation via Ezh2/p53 competition, we demonstrate how GSK126 uniquely empowers research at the intersection of cancer biology, immune modulation, and next-generation therapeutic discovery.
-
GSK126: A Selective EZH2 Inhibitor Transforming Cancer Ep...
2025-10-18
GSK126, a highly selective EZH2/PRC2 inhibitor, empowers researchers to probe and modulate epigenetic regulation in oncology and immunology with unmatched precision. This article delivers actionable protocols, troubleshooting insights, and comparative advantages that set GSK126 apart in cancer epigenetics and inflammasome research.
-
Cisapride (R 51619): Unlocking Dual Pathways in Cardiac a...
2025-10-17
Explore how Cisapride (R 51619), a nonselective 5-HT4 receptor agonist and potent hERG potassium channel inhibitor, is advancing both cardiac electrophysiology and gastrointestinal motility studies. This article reveals distinct research applications, mechanistic insights, and future innovation strategies for this uniquely dual-acting compound.
-
AZD0156: Unlocking ATM Inhibition for Next-Generation Gen...
2025-10-16
Explore how AZD0156, a potent selective ATM kinase inhibitor, is revolutionizing DNA damage response and genomic stability research. This article reveals novel mechanistic insights and translational applications that distinguish AZD0156 from conventional inhibitors.
-
br Conflict of interest statement
2023-07-06
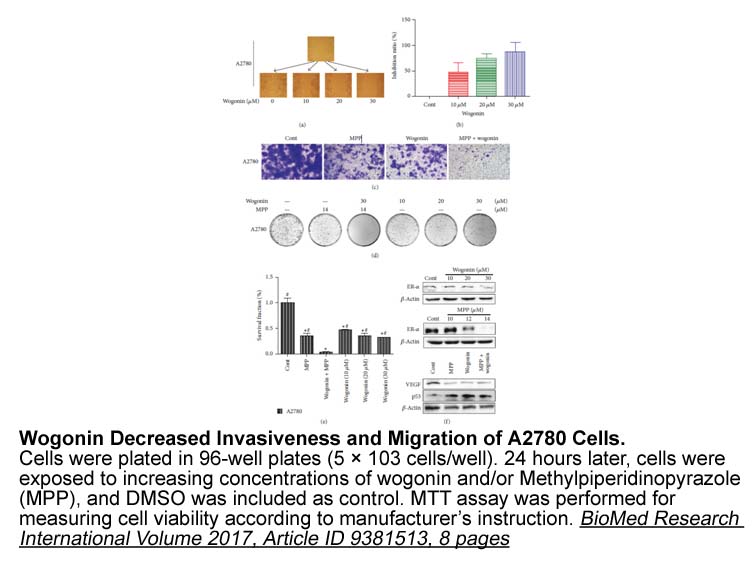
Conflict of interest statement Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a highly complex process characterized by an increased number of epithelial and stromal Oxytocin sale in the transition zone. , , Autopsy studies by McNeal detail the evolution of histological changes within these 2 cellular
-
As mentioned above variation of the
2023-07-06
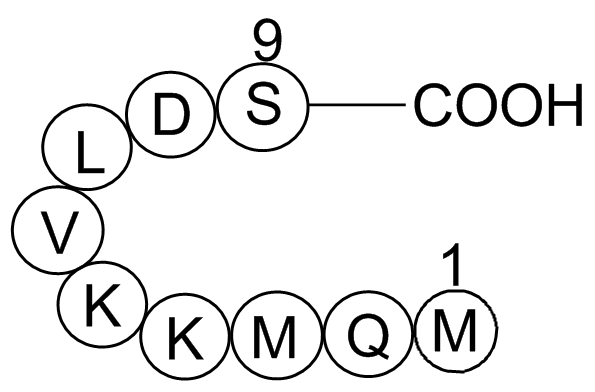
As mentioned above, variation of the A-ring was undertaken in order to improve microsomal stability and kinase selectivity relative to CBR-5884 receptor (). 1-Imidazole-2-carboxamides with substitution at the 4-position (–) were mostly tolerated with 4-cyano-imidazole-2-carboxamide () having compara
-
Foretinib br Materials and methods br Results br Discussion
2023-07-05
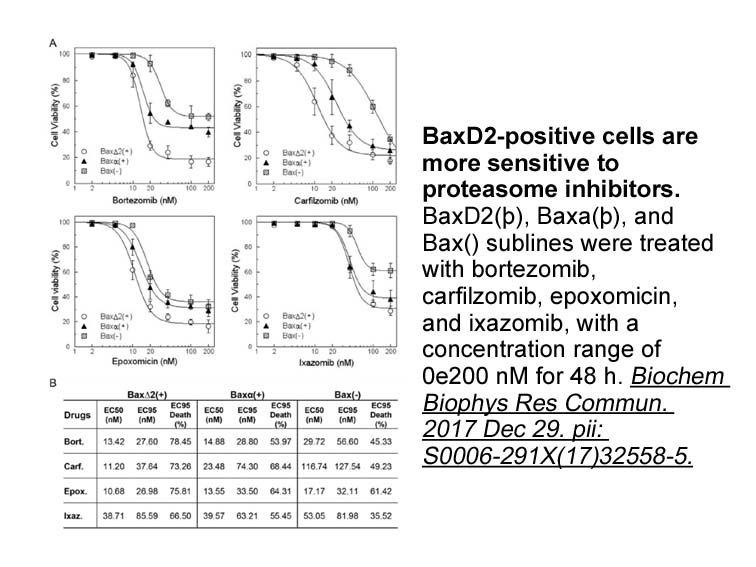
Materials and methods Results Discussion Numerous studies showed that Na+-K+-ATPase activity and membrane Foretinib were decreased in cardiac tissue subjected to IR (Belliard et al., 2013; Lee et al., 2013). In return, treatment that alleviated the progress of IR-related myocardial injury
-
Analyzed by qRT PCR Fig the variation
2023-07-05
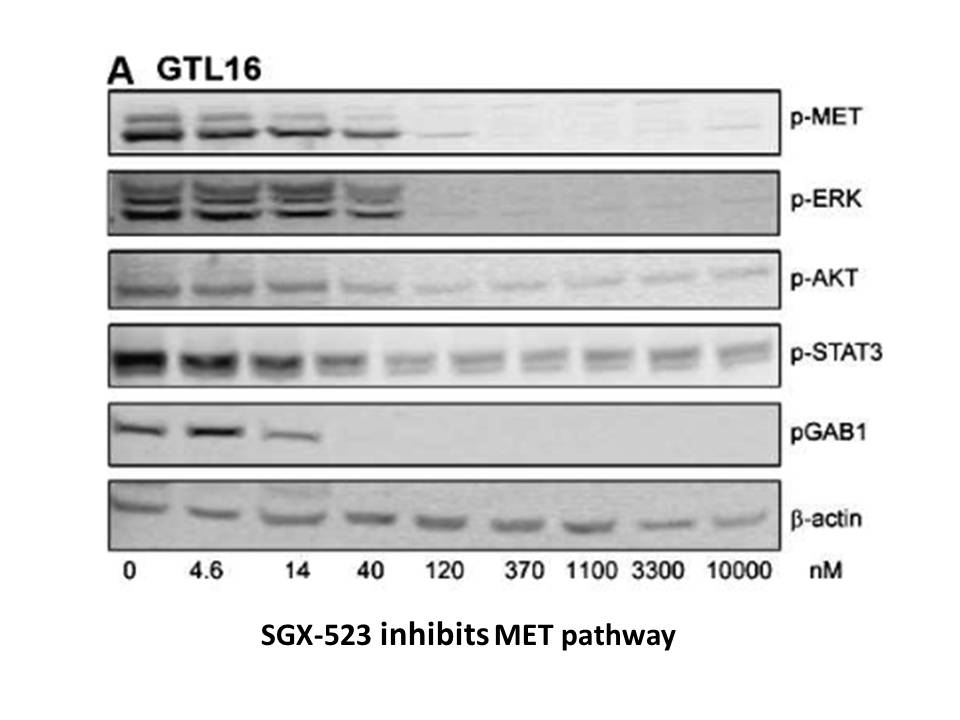
Analyzed by qRT-PCR (Fig. 8), the variation of the expressions of DtACLA and DtACLB was fairly consistent in response to nitrogen deficiency, suggesting that DtACLA and DtACLB may be coordinate to function in the catalysis. It was reported that in Arabidopsis, the coordinated ACLA and ACLB mRNA acc
-
Regulators of the DDR have therefore
2023-07-05
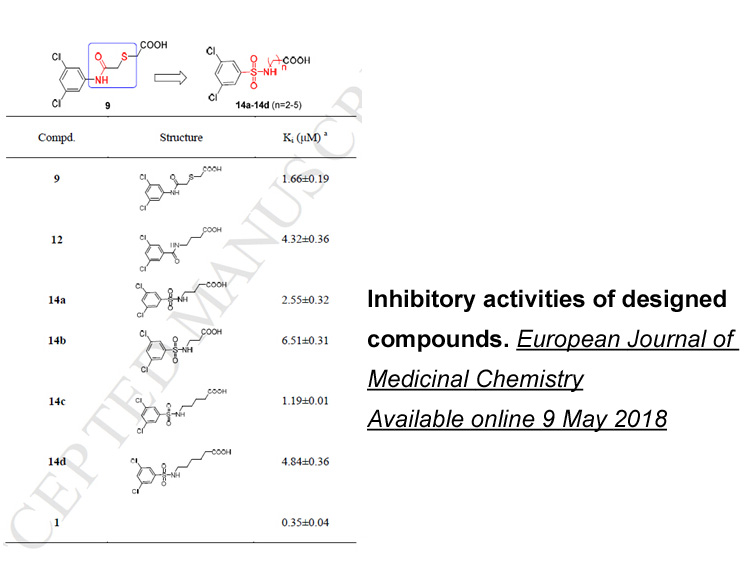
Regulators of the DDR have therefore become attractive targets for cancer therapy primarily through two potential approaches. First, to be used as chemo- or radiosensitisers to increase the effectiveness of standard genotoxic treatments and to help prevent or overcome the development of resistance.
-
The apoptosis promoting Bcl family includes BH only proteins
2023-07-05
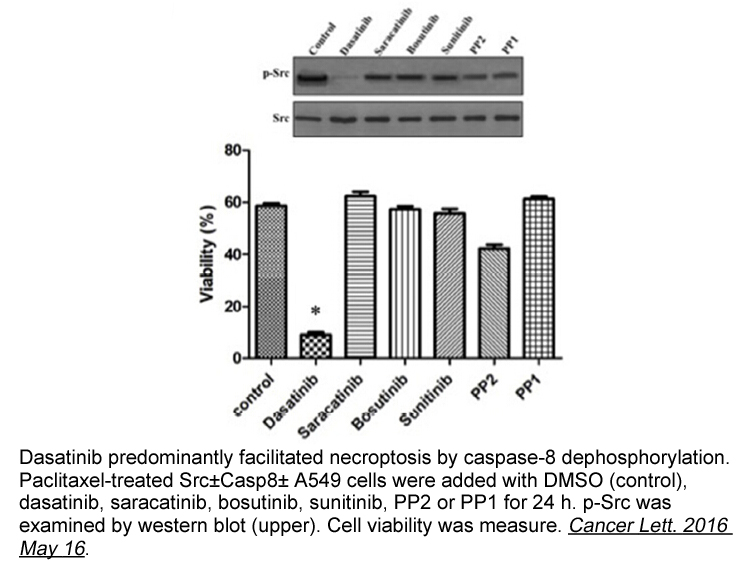
The apoptosis-promoting Bcl-2 family includes BH3-only proteins (e.g., Bim, Bid and Bad) and multiple-domain proteins (e.g., Bax and Bak). At the time of apoptosis stimulation (e.g., DNA damage), only the BH3-only protein is activated, directly or indirectly promoting Bax/Bak oligomerization, changi
-
br Acknowledgment Supported in part by NIH
2023-07-05
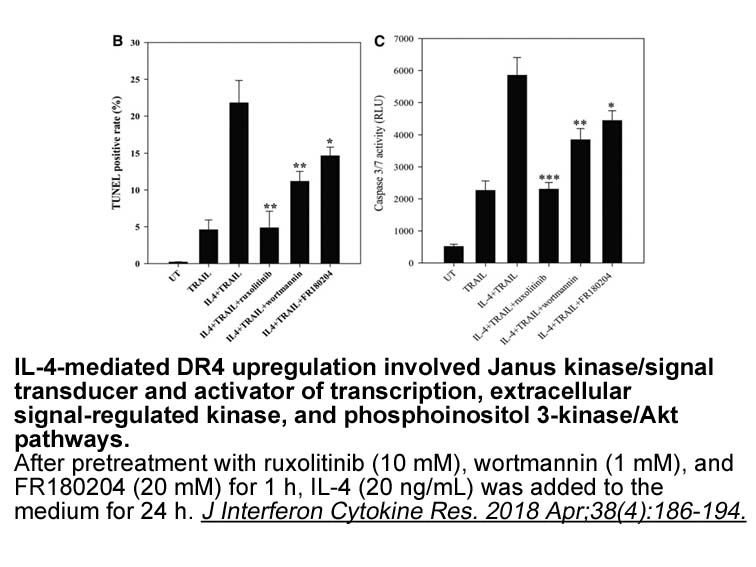
Acknowledgment Supported in part by NIH1R21EB012707 (Biegon, Anat PI). Introduction Estrogens exert pleiotropic effects on a variety of morphological, physiological and behavioral responses in all vertebrate classes ranging from fishes to mammals. Effects of estrogens in the sirtuins concern